103
to earn the huge amount of subsidy so they take part in the kinds of sports held by the government. At the end, the subsidy
shrinks because too many applications. This strategy is that the government would evaluate the then situation and release the
subsidy terms. This method won’t make people to give up their participations due to financial pressure if the budget is limited.
Central health insurance funds
The impacts of sports strategy on future
development of national health insurance
National insurance income : Current
Medical and health insurance expense : Current
The achievement of national preventive healthcare : Current
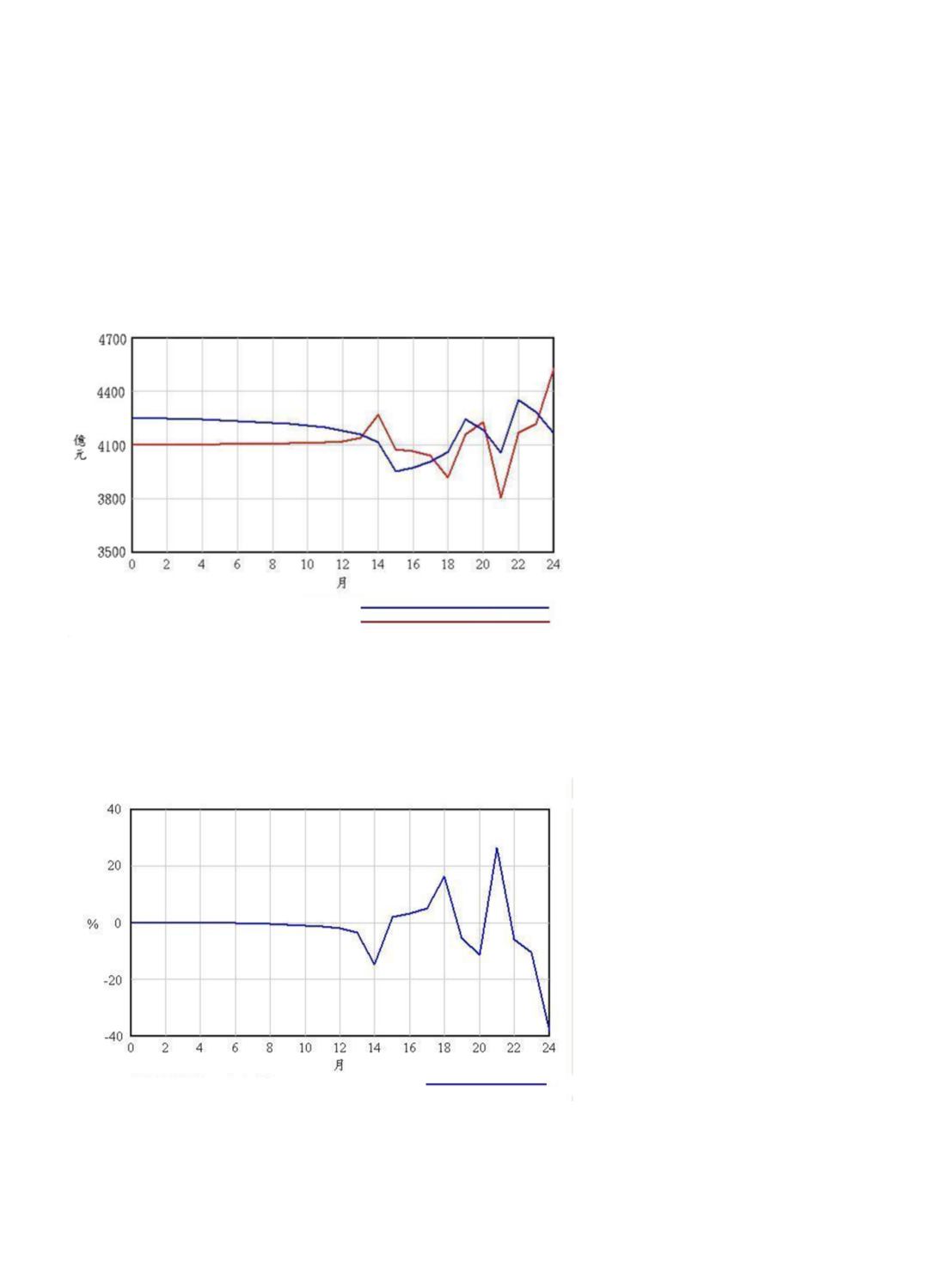
In Figure 7, the development of
national health insurance at the middle
strategy implementation rate become
better from 4% on the early initial
implementation stage up to 65% later
on. Though the progress is unlike that
in the 1st strategy, 79%. However, the
later development appears good and
lasts longer in the near future. This
strategy, unlike the 1st strategy, the
government speeds up to promote the
national health insurance and sports
strategy. As a result, the subsidy is
over-released and too many people
compete to participate. Thus, this good
development could not last too long.
Therefore, this is the problem in the 1st
strategy during the implementation
stage. In the other way, when the
government moderately manage
a budget to implement, this sports
strategy would serve the purpose and
last longer.
In the third strategy situation, we
setup the conditions: low strategy
implementation rate (25%), national
death rate (20%), national physical
strength enhancement rate (5%), and
Figure 8: Central health insurance funds at the low strategy
implementation rate
Figure 9: The development of national health insurance at the low strategy
implementation rate